Pop-Culture’s Got A Chokehold on Your Stocks
In just three short weeks, early in January 2021, Reddit meme-stock traders garnered up enough of GameStop’s stock to increase its value from a mere $17.25 per share to $325 a pop. This reflected almost an 1,800% increase in the stock’s value. In light of this, hedge funds, like New York’s Melvin Capital Management, were left devastated, some smaller hedge funds even went out of business.
For Melvin, because they were holding their GameStop stock in a short position (a trading technique in which the intention is to sell a security with the plan to buy it back later, at a lower cost, in an anticipated short term drop), they lost over 50% of their stock’s value, which translated to nearly $7 billion, in just under a month.
Around 2015, the rise of a new and free online trading platform geared towards a younger generation, emerged in Robinhood. Their mission was simple — “democratize” finance. By putting the capacity to understand and participate in trading, without needing an expensive broker, Robinhood made investing accessible to the masses. However, the very essence of Robinhood putting the power back in the hands of the people, was also what caused a halt in GameStop’s takeover rise. After three weeks, Robinhood had to cease all buying or selling of GameStop’s shares and options because the sheer volume of trading had exceeded their cash-on-hand capacity, or collateral that is required by regulators to function as a legal trade exchange.
But what exactly is a meme-stock? For starters, a meme is an idea or element of pop-culture that spreads and intensifies across people’s minds. As social media has increased in popularity, viral pop-culture references and trends have as well. Memes allow people to instantaneously spread videos, tweets, pictures, or posts that are humorous, interesting, or sarcastic. This in turns goes viral. Meme-stocks therefore originate on the internet, usually in sub-Reddit threads, where users work together to identify a target stock and then promote it. The goal of promoting a meme stock largely involves shorting the stock—as explained above—which means buying, holding, selling, and rebuying as prices fluctuate to turn a profit.
GameStop is not the first, and certainly not the last, stock to be traded in this fashion. But it represents an important shift in the power of social media and its ability to affect the stock market. Another example of the power meme-culture can have on real-world finances and the economy, is Dogecoin.
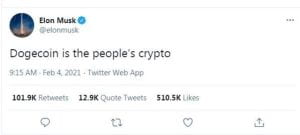
Dogecoin was created as satirical new currency, in a way mocking the hype around existing cryptocurrencies. But its positive reaction and bolstered interest on social media turned the joke crypto into a practical reality. This “fun” version of Bitcoin was celebrated, listed on the crypto exchange Binance, and even cryptically endorsed by Elon Musk. More recently, in 2021, cinema chain AMC announced it would accept Dogecoin in exchange for digital gift card purchases, further bolstering the credibility of this meme-originated cryptocurrency.
Tricks of the Trade, Play at Your Own Risk
Stock trading is governed by the Securities Act of 1933, which boils down to two basic objectives: (1) to require that investors receive financial and other material information concerning securities being offered for public sale; and (2) to prohibit any deceit, misrepresentations, and other fraud in the sale of securities. In order to buy, sell, or trade most securities, it must first be registered with the SEC—the primary goal of registration is to facilitate information disclosures, so investors are informed before engaging. Additionally, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 provides the SEC with broad authority over the securities industry, to regulate, register, and oversee brokerage firms, agents, and SROs. Other regulations at play include the Investment Company Act of 1940 and the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 which regulate investment advisers and their companies, respectively. These Acts require firms and agents that receive compensation for their advising practices are registered with the SEC and adhere to certain qualifications and strict guidelines designed to promote fair, informed investment decisions.
Cryptocurrency has over the years grown from a speculative investment to a new class of assets and regulation is imminent. The Biden Administration has recently added some clarification on crypto use and its regulation through a new directive designating power to the SEC and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), which were already the prominent securities regulators. In the recent Ripple Labs lawsuit, the SEC began to make some strides in regulating cryptocurrency by working to classify it as a security which would bring crypt into their domain of regulation.
Consequentially, the SEC’s Office of Investor Education and Advocacy has adapted with the times and now cautions against making any investment decisions based solely off of information seen on social media platforms. Because social media has become integral to our daily lives, investors are increasingly relying and turning to it for information when deciding when, where, and on what to invest. This has increased the likelihood of scams, fraud, and other misinformation consequences. These problems can arise through fraudsters disseminating false information anonymously or impersonating someone else.

However, there is also an increasing concern with celebrity endorsements and testimonials regarding investment advice. The most common types of social media online scam schematics are impersonation and fake crypto investment advertisements.
With this rise in social media use, the laws governing investment advertisements and information are continuously developing. Regulation FD (Fair Disclosure) provides governance on the selective disclosure of information for publicly traded companies. Reg. FD prescribes that when an issuer discloses any material, nonpublic information to certain individuals or entities, they must also make a public disclosure of that information. In 2008, the SEC issued new guidance allowing information to be distributed on websites so long as shareholders, investors, and the market in general were aware it was the company’s “recognized channel of distribution.” In 2013 this was again amended to allow publishing earnings and other material information on social media, provided that investors knew to expect it there.
This clarification came in light of the controversial boast by Netflix co-founder and CEO Reed Hastings on Facebook that Netflix viewers had consumed 1 billion hours of watch time, per month. Hasting’s Facebook page had never previously disclosed performance stats and therefore investors were not on notice that this type of potentially material information, relevant to their investment decisions, would be located there. Hastings also failed to immediately remedy the situation with a public disclosure of the same information via a press release or Form 8-K filing.
In the same vein, a company’s employees may also be the target of consequence if they like or share a post, publish a third-party link, or friend certain people without permission if any of those actions could be viewed as an official endorsement or means of information dissemination.

The SEC requires that certain company information be accompanied by a disclosure or cautionary disclaimer statement. Section 17(b) of the 1933 Act, more commonly known as the Anti-Touting provision, requires any securities endorsement be accompanied by a disclosure of the “nature, source, and amount of any compensation paid, directly or indirectly, by the company in exchange for such endorsement.”
To Trade, or Not to Trade? Let Your Social Media Feed Decide
With the emergence of non-professional trading schematics and platforms like Robinhood, low-cost financial technology has brought investing to the hands of younger users. Likewise, the rise of Bitcoin and blockchain technologies in the early-to-mid 2010’s have changed the way financial firms must think about and approach new investors. The discussion of investments and information sharing that happens on these online forums creates a cesspool ripe for misinformation breeding. Social media sites are vulnerable to information problems for several reasons. For starters, which posts gain attention is not always something that can be calculated in advance—if the wrong post goes viral, hundreds to thousands to millions of users may read improper recommendations. Algorithm rabbit-holes also pose a risk to extremist views and strategically places ads further on this downward spiral.
Additionally, the presence of fake or spam-based accounts and internet trolls pose an ever more difficult problem to contain. Lastly, influencers can sway large groups of followers by mindlessly promoting or interacting with bad information or not properly disclosing required information. There are many more obvious risks associated but “herding” remains one of the largest. Jeff Kreisler, Head of Behavioral Science at J.P. Morgan & Chase explains that:
“Herding has been a common investment trap forever. Social media just makes it worse because it provides an even more distorted perception of reality. We only see what our limited network is talking about or promoting, or what news is ‘trending’ – a status that has nothing to do with value and everything to do with hype, publicity, coolness, selective presentation and other things that should have nothing to do with our investment decisions.”
This shift to a digital lifestyle and reliance on social media for information has played a key role in the information dissemination for investor decision-making. Nearly 80% of institutional investors now use social media as a part of their daily workflow. Of those, about 30% admit that information gathered on social media has in some way influenced an investment recommendation or decision and another third have maintained that because of announcements they saw on social media, they made at least one change to their investments as a direct result. In 2013, the SEC began to allow publicly traded companies to report news and earnings via their social media platforms which has resulted in an increased flow of information to investors on these platforms. Social media also now plays a large role in financial literacy for the younger generations.
The Tweet Heard Around the Market
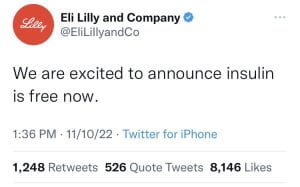
A notable and recent example of how powerful social media warriors and internet trolls can be in relation to the success of a company’s stock came just days after Elon Musk’s acquisition of Twitter and only hours after launching his pay-for-verification Twitter Blue debacle. Insulin manufacturing company Eli Lilly saw a stark drop in their stock value after a fake parody account was created under the guise of their name and tweeted out that “insulin is now free.”

This account acting under the Twitter handle @EliLillyandCo labeled itself, bought a blue check mark, and appended the same logo as the real company to its profile making it almost indistinguishable from the real thing. Consequently, the actual Eli Lilly corporate account had to tweet out an apology “to those who have been served a misleading message from a fake Lilly account.” And clarifying that, “Our official Twitter account is @Lillypad.”
This is a perfect example for Elon Musk and other major companies and CEOs just how powerful pop-culture, meme-culture, and internet trolls are by the simple fact that this parody account casually dropped the stock of a multi-billion dollar pharmaceutical company almost 5% in the matter of a few hours and weaponized with $8 and a single tweet.

So, what does all this mean for the future of digital finance? It’s difficult to say exactly where we might be headed, but social media’s growing tether on all facets of our lives leave much up for new regulation. Consumers should be cautious when scrolling through investment-related material, and providers should be transparent with their relationships and goals in promoting any such materials. Social media is here to stay, but the regulation and use of it are still up for grabs.




 Another e-personator used their verification to impersonate former United States President
Another e-personator used their verification to impersonate former United States President 

 Premiered as a one-night livestream event in January 1 2021, all profits generated from the event were donated to the
Premiered as a one-night livestream event in January 1 2021, all profits generated from the event were donated to the 


 recognizes choreography as a protected form of creative expression, in order to qualify as copyrightable, the choreographic work must conform to the following elements: (1) it is an original work of authorship, (2) it is an expression as opposed to an idea, and (3) it is “fixed in any tangible medium of expression. In addition, the Supreme Court has
recognizes choreography as a protected form of creative expression, in order to qualify as copyrightable, the choreographic work must conform to the following elements: (1) it is an original work of authorship, (2) it is an expression as opposed to an idea, and (3) it is “fixed in any tangible medium of expression. In addition, the Supreme Court has  Office. Registration is deemed to be “made” only when “the Register has registered a copyright after examining a properly filed application.” In an attempt to salvage his claim, Mr. Ribeiro proceeded to the Office but nonetheless left emptied handed. In reviewing the application, the Office refused to grant Mr. Ribeiro a copyright because the Carlton did not rise to the level of choreography since it was a simple routine made up of just three dance steps. Likewise,
Office. Registration is deemed to be “made” only when “the Register has registered a copyright after examining a properly filed application.” In an attempt to salvage his claim, Mr. Ribeiro proceeded to the Office but nonetheless left emptied handed. In reviewing the application, the Office refused to grant Mr. Ribeiro a copyright because the Carlton did not rise to the level of choreography since it was a simple routine made up of just three dance steps. Likewise,  secured a copyright for his choreographic work. Holding that golden ticket, Hanagami argued that Epic Games did not credit or seek his consent to use, display, reproduce, sell or create derivative work based on his registered choreography.
secured a copyright for his choreographic work. Holding that golden ticket, Hanagami argued that Epic Games did not credit or seek his consent to use, display, reproduce, sell or create derivative work based on his registered choreography.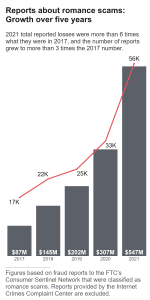 nd would eventually plead guilty to two federal felonies. Glenda was a victim of a Romance Scam and paid the ultimate price.
nd would eventually plead guilty to two federal felonies. Glenda was a victim of a Romance Scam and paid the ultimate price.
 Prevent
Prevent

