Where There’s Good, There’s Bad
Social media’s vast growth over the past several years has attracted millions of users who use these platforms to share content, connect with others, conduct business, and spread news and information. However, social media is a double-edged sword. While it creates communities of people and bands them together, it destroys privacy in the meantime. All of the convenient aspects of social media that we know and love lead to significant exposure of personal information and related privacy risks. Social media companies retain massive amounts of sensitive information regarding users’ online behavior, including their interests, daily activities, and political views. Algorithms are embedded within these functions to promote specific goals of social media companies, such as user engagement and targeted advertising. As a result, the means to achieve these goals conflict with consumers’ privacy concerns.
Common Issues
In 2022, several U.S. state and federal agencies banned their employees from using TikTok on government-subsidized devices, fearful that foreign governments could acquire confidential information. While a lot of the information collected through these platforms is voluntarily shared by users, much of it is also tracked using “cookies,” and you can’t have these with a glass of milk! Tracking cookies allows information regarding users’ online browsing activity to be stored and displayed in a way that targets specific interests and personalizes content tailored to these particular likings. Signing up for a social account and agreeing to the platform’s terms permits companies to collect all of this data.
Social media users leave a “digital footprint” on the internet when they create and use their accounts. Unfortunately, enabling a “private” account does not solve the problem because data is still retrieved in other ways. For example, engagement in certain posts through likes, shares, comments, buying history, and status updates all increase the likelihood that privacy will be intruded on.
and use their accounts. Unfortunately, enabling a “private” account does not solve the problem because data is still retrieved in other ways. For example, engagement in certain posts through likes, shares, comments, buying history, and status updates all increase the likelihood that privacy will be intruded on.
Two of the most notorious issues related to privacy on social media are data breaches and data mining. Data breaches occur when individuals with unauthorized access steal private or confidential information from a network or computer system. Data mining on social media is the process in which user information is analyzed to identify specific tendencies which are subsequently used to inform research and other advertising functions.
Other issues that affect privacy are certain loopholes that can be taken around preventive measures already in place. For example, if an individual maintains a private social account but then shares something with their friend, others who are connected with the friend can view the post. Moreover, location settings enable a person’s location to be known even if the setting is turned off. Other means, such as Public Wi-Fi and websites can still track users’ locations.
Taking into account all of these prevailing issues, only a small amount of information is actually protected under federal law. Financial and healthcare transactions as well as details regarding children are among the classes of information that receive heightened protection. Most other data that is gathered through social media can be collected, stored, and used. Social media platforms are unregulated to a great degree with respect to data privacy and consumer data protection. The United States does have a few laws in place to safeguard privacy on social media but more stringent ones exist abroad.
Social media platforms are required to implement certain procedures to comply with privacy laws. They include obtaining user consent, data protection and security, user rights and transparency, and data breach notifications. Social media platforms typically ask their users to agree to their Terms and Conditions to obtain consent and authorization for processing personal data. However, most are guilty of accepting without actually reading these terms so that they can quickly get to using the app.
Share & Beware: The Law
Privacy laws are put in place to regulate how social media companies can act on all of the information users share, or don’t share. These laws aim to ensure that users’ privacy rights are protected.
There are two prominent social media laws in the United States. The first is the Communications Decency Act (CDA) which regulates indecency that occurs through computer networks. Nevertheless, Section 230 of the CDA provides enhanced immunity to any cause of action that would make internet providers, including social media platforms, legally liable for information posted by other users. Therefore, accountability for common issues on social media like data breaches and data misuse is limited under the CDA. The second is the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA). COPPA protects privacy on websites and other online services for children under the age of thirteen. The law prevents social media sites from gathering personal information without first providing written notice of disclosure practices and obtaining parental consent. The challenge remains in actually knowing whether a user is underage because it’s so easy to misrepresent oneself when signing up for an account. On the other hand, the European Union has General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which grants users certain control over when and how their data is processed. The GDPR contains a set of guidelines that restrict personal data from being disseminated on social media platforms. In the same way, it also gives internet users a long set of rights in cases where their data is shared and processed. Some of these rights include the ability to withdraw consent that was previously given, access information that is collected from them, and delete or restrict personal data in certain situations. The most similar domestic law to the GDPR is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) which was enacted in 2020. The CCPA regulates what kind of information can be collected by social media companies, giving platforms like Google and Facebook much less freedom in harvesting user data. The goal of the CCPA is to make data collection transparent and understandable to users.
online services for children under the age of thirteen. The law prevents social media sites from gathering personal information without first providing written notice of disclosure practices and obtaining parental consent. The challenge remains in actually knowing whether a user is underage because it’s so easy to misrepresent oneself when signing up for an account. On the other hand, the European Union has General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which grants users certain control over when and how their data is processed. The GDPR contains a set of guidelines that restrict personal data from being disseminated on social media platforms. In the same way, it also gives internet users a long set of rights in cases where their data is shared and processed. Some of these rights include the ability to withdraw consent that was previously given, access information that is collected from them, and delete or restrict personal data in certain situations. The most similar domestic law to the GDPR is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) which was enacted in 2020. The CCPA regulates what kind of information can be collected by social media companies, giving platforms like Google and Facebook much less freedom in harvesting user data. The goal of the CCPA is to make data collection transparent and understandable to users.
Laws on the state level are lacking and many lawsuits have occurred as a result of this deficiency. A class action lawsuit was brought in response to the collection of users’ information by Nick.com. These users were all children under the age of thirteen who sued Viacom and Google for violating privacy laws. They argued that the data collected by the website together with Google’s stored data relative to its users was personally identifiable information. A separate lawsuit was brought against Facebook for tracking users when they visited third-party websites. Individuals who brought suit claimed that Facebook was able to personally identify and track them through shares and likes when they visited certain healthcare websites. Facebook was able to collect sensitive healthcare information as users browsed these sites, without their consent. However, the court asserted that users did indeed consent to these actions when they agreed to Facebook’s data tracking and data collection policies. The court also stated that the nature of this data was not subject to any stricter requirements as plaintiffs claimed it was because it was all available on publicly accessible websites. In other words, public information is fair game for Facebook and many other social media platforms when it comes to third-party sites.
were all children under the age of thirteen who sued Viacom and Google for violating privacy laws. They argued that the data collected by the website together with Google’s stored data relative to its users was personally identifiable information. A separate lawsuit was brought against Facebook for tracking users when they visited third-party websites. Individuals who brought suit claimed that Facebook was able to personally identify and track them through shares and likes when they visited certain healthcare websites. Facebook was able to collect sensitive healthcare information as users browsed these sites, without their consent. However, the court asserted that users did indeed consent to these actions when they agreed to Facebook’s data tracking and data collection policies. The court also stated that the nature of this data was not subject to any stricter requirements as plaintiffs claimed it was because it was all available on publicly accessible websites. In other words, public information is fair game for Facebook and many other social media platforms when it comes to third-party sites.
In contrast to these two failed lawsuits, TikTok agreed to pay a $92 million settlement for twenty-one combined lawsuits due to privacy violations earlier this year. The lawsuit included substantial claims, such as allegations that the app analyzed users’ faces and collected private data on users’ devices without obtaining their permission.
$92 million settlement for twenty-one combined lawsuits due to privacy violations earlier this year. The lawsuit included substantial claims, such as allegations that the app analyzed users’ faces and collected private data on users’ devices without obtaining their permission.
We are living in a new social media era, one that is so advanced that it is difficult to fully comprehend. With that being said, data privacy is a major concern for users who spend a large amount of time sharing personal information, whether they realize it or not. Laws are put in place to regulate content and protect users, however, keeping up with the growing presence of social media is not an easy task–sharing is inevitable and so are privacy risks.
To share or not to share? That is the question. Will you think twice before using social media?











 Children, however, are
Children, however, are 
 Omegle is a free video-chatting social media platform. Its primary function has become meeting new people and arranging “
Omegle is a free video-chatting social media platform. Its primary function has become meeting new people and arranging “

 found that Section 230 immunity did not apply to Omegle in a
found that Section 230 immunity did not apply to Omegle in a 
 The sweeping transformation of social media platforms over the past several years has given rise to convenient and cost-effective advertising. Advertisers are now able to market their products or services to consumers (i.e. users) at
The sweeping transformation of social media platforms over the past several years has given rise to convenient and cost-effective advertising. Advertisers are now able to market their products or services to consumers (i.e. users) at 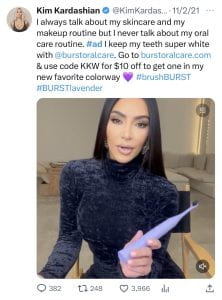 should
should  drink, Muse in a
drink, Muse in a 
 The
The 





 demand. This conduct is not illegal, but it negates the potential revenue these industries may obtain. Such a solution was, is, and consistently will be recognized as legal activity.
demand. This conduct is not illegal, but it negates the potential revenue these industries may obtain. Such a solution was, is, and consistently will be recognized as legal activity. 











 Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (“ADHD”) is an example of a condition that social media has jumped on. #ADHD has
Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (“ADHD”) is an example of a condition that social media has jumped on. #ADHD has /cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23973837/adhd_ads.jpg)