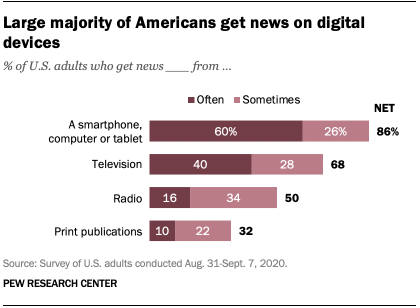
Social media law has become somewhat of a contentious issue in recent years. While most people nowadays could not imagine life without it, many realize too, that it’s influence on our daily lives may not be a great thing. As the technology has advanced to unimaginable levels and the platforms have boomed in popularity, it seems as though our smart phones and Big Tech know our every move. The leading social media platform, Facebook, has around 1.82 billion active users a day, with people volunteering all sorts of personal information to be stored in the internet database. Individual profiles hold pictures of our children, our friends, our family, meals we eat, locations we visit. “What’s on your mind?” is the opening invite to any Facebook page, and one can only hazard a guess as to how many people actually answer that question on a daily basis. Social media sites know our likes, our dislikes, our preferences, our moods, the shoes we want to buy for that dress we are thinking of wearing to the party we are looking forward to in three weeks!
With all that knowledge, comes enormous power, and through algorithmic design, social media can manipulate our thoughts and beliefs by controlling what we see and don’t see. With all that power, therefore, should come responsibility, but Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act (CDA) has created a stark disconnect between the two. What started out as a worthy protection for internet service providers for the content posted by others, has more recently drawn criticism for the lack of accountability held by social media oligarchs such as Jack Dorsey (Twitter) and Mark Zuckerberg (Facebook).
However, that could all be about to change.
On May 28, 2017, three friends lost their lives in a deadly car accident in which the 17-year-old driver, Jason Davis, crashed into a tree at an estimated speed of 113 mph. Landen Brown, 20, and Hunter Morby, 17, were passengers. Tragic accident? Or wrongful death?
Parents of the deceased lay blame on the Snapchat App, which offered a ‘Speed Filter’ that would clock how fast you were moving, and allowed users to snap and share videos of their movements in progress.
You see where this is going.
As quickly became the trend, the three youths used the app to see how fast they could record the speed of their car. Just moments before their deaths, Davis had posted a ‘snap’ clocking the car’s speed at 123 mph. In Lemmon v Snap, the parents of two of the boys brought suit against the social media provider, Snap, Inc., claiming that the app feature encouraged reckless driving and ultimately served to “entice” the young users to their death.
Until now, social media platforms and other internet service providers have enjoyed the protection of near absolute immunity from liability. Written in 1996, Section 230 was designed to protect tech companies from liability, for suits such as defamation, for third party posts. In the early days, it was small tech companies, or an online business with a ‘comments’ feature that generally saw the benefits of the Code. 25 years later, many people are questioning the role of Section 230 within the vastly developing era of social media and the powerful pass it grants Big Tech in many of its societal shortcomings.
Regarded more as an open forum than the publisher or speaker, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, Instagram and Snapchat, have been shielded by Section 230 from any legal claims of harm caused by the content posted on their sites.
Applied broadly, it is argued that Section 230 prevents Snap, Inc. from being held legally responsible for the deaths of the three boys in this case, which is the defense the tech company relied upon. The district court dismissed the case on those grounds, holding that the captured speeds fall into the category of content published by a third party, for which the service provider cannot be held liable. The Ninth Circuit however, disagrees. The Court’s interesting swerve of such immunity, is that the speed filter resulted in the deaths of the boys regardless of whether or not their captured speeds were posted. In other words, it did not matter if the vehicle’s speed was shared with others in the app; the fact that the app promotes, and rewards, high speed (although the award system within the app is not entirely clear), is enough.
The implications of this could be tremendous. At a time when debate over 230 reevaluations is already heavy, this precedential interpretation of Section 230 could lead to some cleverly formulated legal arguments for holding internet service providers accountable for some of the highly damaging effects of internet, social media and smart phone usage.
For the many benefits the internet has to offer, it can no longer be denied that there is another, very ugly side to internet usage, in particular with social media.
It is somewhat of an open secret that social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram, purposely design their apps to be addictive by its users. It is also no secret that there is a growing association between social media usage and suicides, depression and other mental health issues. Cyber bullying has long been a very real problem. In addition, studies have shown that smart device screen time in very young children has shockingly detrimental impacts on a child’s social and emotional developments, not to mention the now commonly known damage it can have on a person’s eyesight.
An increased rate of divorces has been linked to smart phones, and distracted driving – whether it be texting or keeping tabs on your Twitter retweets, or Facebook ‘likes’– is on the increase. Even an increase in accidents while walking has been linked to distractions caused by the addictive smart devices.
With the idea of accountability being the underlying issue, it can of course be stated that almost all of these problems should be a matter of personal responsibility. Growing apart from your spouse? Ditch your cell phone and reinvent date night. Feeling depressed about your life as you ‘heart’ a picture of your colleague’s wine glass in front of a perfect sunset beach backdrop? Close your laptop and stop comparing yourself to everyone else’s highlights. Step in front of a cyclist while LOL’ing in a group text? Seriously….put your Apple Watch hand in your pocket and look where you are going! The list of personal-blame is endless. But then we hear about three young friends, two still in their teens, who lose their lives engaged with social media, and suddenly it’s not so easy to blame them for their own devastating misfortune.
While social media sites cannot be held responsible for the content posted by others, no matter how hurtful it might be to some, or no matter what actions it leads others to take, should they be held responsible for negligently making their sites so addictive, so emotionally manipulative and so targeted towards individual users, that such extensive and compulsive use leads to dire consequences? According to the Ninth Circuit, negligent app design can in fact be a cause of action for wrongful death.
With a potential crack in the 230-armor, the questions many lawyers will be scrambling to ask are:
-
-
- What duties do the smart device producers and/or internet service providers owe to their users?
- Are these duties breached by continuing to design, produce, and provide products that are now known to create such disturbing problems?
- What injuries have occurred and where those injuries foreseeably caused by any such breaches of duty?
For the time being, it is unlikely that any substantial milestone will be reached with regards to Big Tech accountability, but the Ninth Circuit decision in this case has certainly delivered a powerful blow to the Big Tech apparent untouchability in the courtroom.
As awareness of all these social media related issues grow, could this court decision open the door to further suits of defective or negligent product design resulting in death or injury? Time will tell…..stay tuned.








:focal(1435x1214:1436x1215)/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/b0/ad/b0ad80d1-737e-4368-b02e-81558703cc89/istock-1151157687.jpg)

