Category: Social Media, YouTube, Money, Profits, Child Labor Laws
Dear loyal followers: will you endorse this product for me?

Hi, lambs. It’s me, your Gram celeb. Who wouldn’t like to start their day with a bowl of oatmeal with these freshly picked berries? Remember that I’m always with you, lambs. #yummy #healthybreakfast #mylifestyle #protein #Thanks XYZ.
Up to this point, you may think that your Instagram celebrity wants to share a healthy breakfast with you. You may even feel pleased to see that your celebrity took the time to post such a personal picture, until you read further:
Thank you, XYZ Company, for your healthy breakfast delivery. Love, XOXO.
While some people feel nonchalant about promoted products, some followers may feel betrayed to know that their celebrities are only using their accounts to earn money. You feel tired of seeing these sponsored posts. Are there any legal actions against the Instagram celebrity to melt your deceived heart?
What’s so disturbing and tricky about Instagram influencer marketing is that users cannot always detect whether they are being exposed to digital advertising.
According to an Instagram internal data research, approximately 130 million accounts tap on shopping posts every month. There are a plethora of guides on digital marketing for rising influencers, and one of the highest noted tips is to advertise a product with storytelling. The main theme is to advertise as naturally as possible to make consumers feel engaged—and subsequently, have them make a purchase.
In Jianming Jyu v. Ruhn Holdings Ltd., the court held that social media has become so influential that being a social media influencer is now recognized as a profession. The court defined social media influencers as “individuals who create content on social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, Tik Tok, and Instagram with the hope of garnering a large public following [and] who are paid to promote, market and advertise products and services to their fans and followers.” Id.
Take this as another example: your cherished, ever-so-harmless Instagram mega-celebrity wore a beautiful Gucci belt. The celebrity mentioned that the same belt was available on Amazon, which was on sale for less than a quarter of the actual price at Gucci. You immediately purchased the belt, thanking your celebrity and yourself for following the celebrity. Upon the belt’s arrival, you realized that the belt was conspicuously fake with the brand named Pucci. On November 12, 2020, Amazon sued 13 individuals and businesses (collectively, the “defendants”) for advertising, promoting, and facilitating the sale of counterfeit luxury goods on Amazon. The defendants used their Instagram and other social media accounts to promote their knockoff goods being sold on Amazon. Amazon stated that they are seeking damages and an injunction against the influencers to bar them from using Amazon. As of July 4, 2021, the case is still pending.
Okay, we get it. But that’s something Instagram celebrities have to resolve. What about us, the innocent lambs?
Are there any legal actions on digital marketing? Yes!
A digital advertising claim may be brought in state or federal court or action brought by a federal administrative agency, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). Generally, Instagram advertising is considered online advertising, which the FTC regulates. The FTC Act prohibits deceptive advertising in any medium. That is, “advertising must tell the truth and not mislead consumers.” A claim can be misleading if relevant information is left out or if the claim implies something that is not true. So, if an influencer promotes a protein bar that says it has 20 grams of protein, but it actually had 10 grams of protein, it is misleading.
Furthermore, the FTC Act states that all advertising claims must be “substantiated,” primarily when they concern “health, safety, or performance.” If the influencer quoted the protein bar company, which stated that there was research that their protein bar lowered blood pressure, the FTC Act requires a certain level of support for that claim. Thus, online influencers are liable for the products they endorse on social media platforms.
Wait, there is one more. Due to the growing number of fraudulent activities on Instagram, the FTC released new regulations targeted at Instagram influencers. According to 16 CFR § 255.5, the FTC requires that an influencer shall “clearly and conspicuously disclose either the payment or promise of compensation prior to and in exchange for the endorsement or the fact that the endorser knew or had reason to know or to believe that if the endorsement favored the advertised product some benefit.” In sum, an influencer must disclose that the post is sponsored. The FTC noted that the hashtags like “partner,” “sp,” “thanks [Brand]” are not considered adequate disclosures. Otherwise, it is a violation subject to penalty.

Simply putting hashtag “ad” is not an option
The marketing Mediakix issued a report on top celebrity Federal Trade Commission compliance for sponsored posts and found that 93% of the top Instagram endorsements did not meet the FTC’s guidelines.
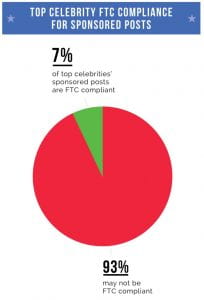
Going back to the oatmeal example, using the hashtag “#Thanks XYZ” is not sufficient to show that the post is sponsored, and the celebrity is subject to penalty.
As a rule of thumb, all Instagram sponsorships must be disclosed no matter what, and the disclosures must be clear about the sponsorship. Playing hide-and-seek with hashtags is never an option.
What is your opinion on digital marketing? If you were a legislator, what should the regulation on digital marketing be?
How One Teenager’s Snapchat Shaped Students Off-Campus Free Speech Rights
Did you ever not make your high school sports team or get a bad grade on an exam? What did you do to blow off steam? Did you talk to your friends or parents about it or write in your journal about it? When I was in High school- some of my classmates would use Twitter or Snapchat to express themselves. However, the rates for the use of smartphones and social media were much lower than they are today. For instance, today high school students use their smartphones and social media at an incredibly high rate compared to when I was in high school almost ten years ago. In fact, according to Pew Research Center, 95% of teenagers have access to smartphones and 69% of teenagers use Snapchat. This is exactly why the recent Supreme Court decision on Mahanoy Area School District v. B.L. is more important than ever, as it pertains to student’s free speech rights and how much power schools have in controlling their student’s off-campus speech. Further, this decision is even more necessary because the last time the Supreme Court ruled on student’s free speech was over fifty years ago in Tinker v. Des Moines, way before anyone had smartphones or social media. Therefore, the latest decision by the Supreme Court will shape the future of the power of school districts and the first Amendment rights for students for maybe the next fifty years.
The main issue in Mahanoy Area School District v. B.L. is whether public schools can discipline students over something they said off-campus. The facts in this case, occurred when Levy, was a sophomore at Mahoney Area School District. Levy didn’t make the varsity cheerleading team; naturally, she was upset and frustrated about the situation. So, that weekend, Levy was at the convenience store in town with a friend. Levy and the friend took a Snap Chat with their middle finger raised with the caption “F- School, F-Softball, F-Cheerleading, F-Everything” and sent it to her Snap Chat friends. Then, the picture was screenshotted and shown to the cheerleading coach. Which lead to Levy being suspended from the cheerleading team for one year.
Furthermore, Levy and her parents did not agree with the suspension and the school’s involvement in Levy’s off-campus speech. Therefore, Levy and her parents filed a lawsuit claiming their suspension violated Levy’s First Amendment free speech rights. Levy sued the school under 42 U.S.C. § 1983 alleging (1) that her suspension from the team violated the First Amendment; (2) that the school and team rules were overbroad and viewpoint discriminatory; and (3) that those rules were unconstitutionally vague. The district court granted summary judgment in favor of Levy, stating that the school had violated her First Amendment rights. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit affirmed the district court decision. The Mahoney School District petitioned for a writ of certiorari.
In an 8-1 decision the Supreme Court ruled in favor of Levy. The Supreme Court held that the Mahoney Area School District violated Levy’s First Amendment rights by punishing her for using vulgar language that criticized the school on social media. The Supreme Court noted numerous reasons why they ruled in favor of Levy. Additionally, The Supreme Court noted the importance of schools monitoring and punishing some off-campus speech. Such as, speech and behavior that is “serious or severe bullying or harassment targeting particular individuals; threats aimed at teachers or other students.” This is more necessary than ever before due to the increase in online bullying and harassment; that can impact the day-to-day activities of the school and the development of minors.
While it’s important in some circumstances for schools to monitor and address off-campus speech. The Supreme Court noted three reasons that would limit schools from interfering with student’s off-campus speech. First, a school, concerning off-campus speech, will rarely stand in loco parentis. Therefore, schools do not have more authority than parents. Especially not for off-campus speech. The parent is the authority figure; and will decide to discipline or not in most activities in their child’s life, especially what happens outside of school. This is important because parents have the authority to raise and discipline their children the way they believe, not based on the school district’s beliefs.
Second, “from the student perspective, regulations of off-campus speech, when coupled with regulations of on-campus speech, include all the speech a student utters during the full 24-hour day.” There would be no boundaries or limitations to what the school district would be allowed to discipline their students on. For instance, what if a group of students on a Saturday night decided to make a Tik Tok, and during the Tik Tok, the students curse and use vulgar language, would they be in trouble? If there were no limits to what the school could punish for off-campus speech, then those students could be in trouble for their Tik Tok video. Therefore, it’s important that the Supreme Court made this distinction to protect the student Frist Amendment rights.
Finally, the third reason is the school itself has an interest in protecting a student’s unpopular expression, especially when the expression takes place off-campus.” For instance, the Supreme Court stated that if schools did not protect their students’ unpopular opinions, this would limit and ruin the student’s ability to express themselves and schools are a place for students to learn and create their own opinion- even if that opinion differs from the school’s. To conclude, this would severely impact the student’s ability to think for themselves and create their own opinion, and respect other’s opinions that differ from their own.
Overall, I agree with the Supreme Court’s decision in this case. I believe it’s essential to separate in-school speech and off-campus speech. However, the only time off-campus speech should be monitored and addressed by the school is if there is bullying, harassing, or threatening language against the school, groups, or individuals at the school. With that being said, the Supreme Court noted three very important reasons as to why the public schools cannot have full control of students’ off-campus speech. All three of these reasons are fair and justifiable to protect the parents and students from being overly controlled by the school. To conclude, there is still a lot of questions and uncertainty, especially since technology is rapidly advancing and new social media platforms emerging frequently. I am curious if the Supreme Court will rule on a similar within the next fifty years and how this will impact schools in the next few years.
Do you agree with the Supreme Court decision and how do you see this ruling impacting public schools over the next few years?
Is social media promoting or curbing Asian hate?

The COVID-19 pandemic has caused our lives to twist and turn in many unexpected ways. Of all the ethnicities in the world, the Asian population took the hardest hit since the virus originated from China. This ultimately caused a significant increase in hate crimes, particularly towards the Asian community, in the real world as well as the cyber world. Since the number of internet users is almost uncountable, the impact that it creates online, as well as offline, is massive. Social media can create bias and social media has the power to remedy bias. The question becomes which side of the scale is it currently tipping towards? Is the internet making social network platform users more vulnerable to manipulation? Are hatred and bias “contagious” through cyber means? On the contrary, is social media remedying the bias that people have created through the internet?
Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act governs the cyber world. It essentially provides legal immunity to internet providers such as TikTok, Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat and etc. The Act states: “No provider or user of an interactive computer service shall be treated as the publisher or speaker of any information provided by another information content provider.” With that being said, posts and comments that appear on these social media platforms do not have any legal ramifications for the tech companies. Hence, do these tech companies have incentives to regulate what is posted on their websites? With the Asian hate wave currently going on, will it evolve into a giant snowball of problems if social media platforms fail to step in? On the other hand, if these tech companies elect to step in, to what extent can they regulate or supervise?
The hatred and bias sparked by the pandemic have not been limited to the real world. Asian Americans have reported the biggest increase in serious incidents of online hate and harassment throughout such a crazy time. Many of them were verbally attacked or insulted by racist and xenophobic slurs merely because they have Asian last names or that they look Asian. According to a new survey shared exclusively with USA TODAY, comparing to last year, there was an 11% increase in sexual harassment, stalking, physical threats, and other incidents reported by Asian Americans, of which many were through online social media platforms. Pursuant to the findings by the Center for the Study of Hate and Extremism at California State University, hate crimes against Asian Americans rose 149% from 2019 to 2020. That is 149% in one year. In addition, an AI-based internet abuse detection organization named L1ght reported a 900% increase on Twitter since the start of this pandemic. This may just be the tip of an iceberg as many of the hate crime incidents may have gone unreported. As you may recall, former President Trump publicly referred the COVID-19 coronavirus as the “Chinese Virus” which led to a record-breaking level of brutal online harassment against Asian Americans. This also gave rise to other similar remarks such as “Kung Flu” or “Wuhan Virus.” Social media users began using hashtags of the like. Just the hashtag “#ChineseVirus” alone has been used over 68,000 times on Instagram.
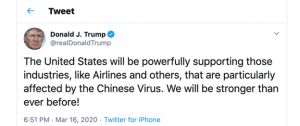
We must not forget that the real world and the cyber world are interconnected. Ideas consumed online can have a significant impact on our offline actions which may lead to violence. Last week, I had the privilege to interview New York Police Department Lieutenant Mike Wang who is in charge of the NYPD’s Asian Hate Crimes Task Force in Brooklyn, he expressed his concerns about the Asian community being attacked, seniors in particular. Lieutenant Wang said during the interview: “It’s just emotionally difficult and heartbreaking. New York Police Department is definitely taking unprecedented measures to combat these crimes. These incidents cannot be overlooked.” Most of these incidents were unprovoked. Some examples include an elderly Thai immigrant who died after being shoved to the ground, a Filipino-American citizen being slashed in the face with a box cutter leaving a big permanent scar on his face, a Chinese lady being slapped and then set on fire, as well as six Asian-Americans being brutally shot to death in a spa one night. Wang indicated that crimes against Asian-Americans in general are nothing new, they have been in existence for quite some time; however, the rage and frustration of the COVID-19 pandemic fueled this fire to an uncontrollable level. Wang encourages citizens to report crimes in general, not just hate crimes, as we need to be more vocal. You can read more about hate crimes and bias on the city’s website.

From verbal harassment to physical assaults, there have been thousands of reported cases since the pandemic started. These are typically hate crimes as offenders believe that the Asian population should be blamed for the spread of the virus. Perhaps people’s daily interactions online play an important role here. Almost everyone uses some sort of social network in our country, the more hatred and bias they see online, the more likely they will exhibit violence in real life. Why? Because people would think such behaviors are acceptable since many others are doing it. Accountability does not seem to be an issue, especially through social channels. At the most, the user’s post would be removed or the account would get suspended. With that being said, it is questionable as to whether the tech companies are doing enough to address these issues? When encountering these hateful behaviors in the cyber world, what are the policies of the social media giants? For instance, Twitter has implemented a policy on hate speech that prohibits accounts whose primary purpose was to incite harm towards others. Twitter does reserve the discretion to remove inappropriate content or suspend users who violated their policy. You can read more about their Hateful Conduct Policy on their website. Other social media platforms such as Facebook, TikTok, and YouTube all have similar policies in place to address hateful behaviors, violent threats, and harassment; however, are they sufficient? According to the CEO of the Anti-Defamation League, online users continue to experience strong hateful comments despite that the social network companies alleged that they are taking things seriously. Facebook and YouTube are still allowing users to use the racially incentive term “Kung Flu” while TikTok has prohibited it. A comics artist Ethan Van Sciver joked about killing Chinese people in one of his videos but later claimed that it was “facetious sarcasm.” YouTube only removed the video stating that it was a violation of its hate speech policy. Like I previously mentioned, the accountability with these social networks is minimal.

Social networks have definitely helped spread the news keeping everyone in the country informed about the horrible incidents that are happening on a regular basis. Other than spreading the virus of hatred and bias online, social networks also raise awareness and promote positivity on the other hand. As Asian hate crimes spike, public figures, and celebrities are taking part to stand against this battle. Allure magazine’s editor-in-chief Michelle Lee and designer Phillip Lim are one of them. They have posted videos on Instagram sharing their very own experiences of racism in an effort to raise awareness. They also used the hashtag #StopAsianHate in their posts. On March 20, 2021, “Killing Eve” star Sandra Oh joined a “Stop Asian Hate” protest in Pittsburgh. She said she is “proud to be Asian” while giving a powerful speech urging people to fight against racism and hatred towards the Asian community. The video of her speech went viral online in just a day and there have been more than ninety-three thousand views on YouTube since. I have to say that our generation is not afraid to speak up about the hate and injustice we face in our society today. This generation is taking it upon ourselves to prove racism instead of relying on authorities to recognize the threats and implement policy changes. This is how #StopAAPIHate came about. The hashtag stands for “Stop Asian American and Pacific Islander Hate.” Stop AAPI Hate is a nonprofit organization that tracks incidents of hate and discrimination against Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders in the United States. It was recently created as a social media platform to bring awareness, education, and resources to the Asian community and its allies. Stop AAPI Hate also utilized social networks like Instagram to organize support groups, provide aid and pressure those in power to act. The following is a list of influential members of the AAPI community who are vocalizing their concerns and belief: Christine Chiu, “The Bling Empire” star who is also a producer and an entrepreneur; Chriselle Lim, who is a digital influencer, content creator and entrepreneur; Tina Craig, who is the founder and CEO of U Beauty; Daniel Martin, who is the makeup artist and global director of Artistry & Education at Tatcha; Yu Tsai, who is a celebrity and fashion photographer & host; Sarah Lee and Christine Chang, who are the co-founders and co-CEOs of Glow Recipe; Aimee Song, who is an entrepreneur and digital influencer; Samuel Hyun, who is the chairman of the Massachusetts Asian American Commission; Daniel Nguyen who is an actor; Mai Quynh, who is a celebrity makeup artist; Ann McFerran, who is the founder and CEO of Glamnetic; Nadya Okamoto, who is the founder of August; Sharon Pak who is the founder of INH; Sonja Rasula, who is the founder of Unique Markets; as well as Candice Kumai, who is a writer, journalist, director and best-selling author. The list can go on but the purpose of these influential speakers is that taking things to social media is not just about holding people or companies accountable, instead, it is about creating meaningful changes in our society.

The internet is more powerful than we think it is. It is dangerous to allow individuals to attack or harass others, even through the screen. I understand that the social media platforms cannot blatantly censor contents or materials as they see inappropriate on their websites as it may be a violation of the user’s First Amendment rights; however, there has to be more that they can do. Perhaps creating more rigorous policies as an effort to combat hate speech. If we are able to track the user’s identity to his or her real-life credentials, it may curb the tendency of potential offenders or repeated offenders. The question is how do you draw the line between freedom of speech and social order?
Trapped in Virtual Reality!
Millions of people went crazy for Pokemon GO in 2016, venturing into private and public locations to catch Pokemon characters that were only visible to them. The game Pokémon GO was the first to introduce the public to the concept of augmented reality (AR).

AR users can see the real world as it is, but with visible digital images overlayed such that the images appear to be part of the real environment.
There’s also virtual reality, which goes beyond augmented reality (VR). Users can enter a virtual environment and move around and interact with it as if it were the real world by wearing a headset.
“Around 25 million people in the United States consider themselves to be active video gamers. The sector is worth $30 billion in the United States and $90 billion globally. It has its own popular television network, Twitch.tv, and in 2015, the finals of a League of Legends tournament drew more viewers than the NBA basketball finals. In the last year, over $1 billion in income was produced by Pokémon Go alone.”
AR and VR, on the other hand, raise legal issues for courts, businesses, and users. People will use AR and VR to kill and die, and some have already done so. They will harm themselves as well as others. Players have already fallen down a cliff or walked into oncoming traffic while playing Pokémon GO. Some will take advantage of the technology to threaten or scam others. To determine who is to blame, courts will need to grasp the technology and how it varies from the world before it.
CRIMES. In the real world, people sexually harass strangers and expose themselves indecently; there’s no reason why they wouldn’t do it in virtual reality. They are undoubtedly more likely to do so if they believe it will be difficult for law authorities to apprehend them. That ambition, though, may be difficult to fulfill. Extradition’s additional hurdles are likely to outweigh the greater ease of proving. As a result, traditional police forces may effectively ignore numerous VR street crimes. Suspension or exclusion from the virtual reality environment will most likely be the consequences. Participants who have been kicked off can simply re-enter by generating a new user ID.
The exhibitionist would almost probably be charged with indecent exposure or public lewdness if this happened in real life. Is it possible to apply the same law to virtual reality? Would you expect police forces to welcome the prospect of extraditing a person from another state or county simply because their internet avatar is nude? Because the exchanges may occur in multiple physical jurisdictions, it will be more difficult to regulate them effectively. As a result, police arrests and prosecutions will become more expensive, and law enforcement will be less willing to intervene. This is especially true in circumstances where there appears to be no “real” harm. As a result, police will be less likely to take this issue seriously, leaving VR users to fend for themselves.
We may see crimes and other issues occur in VR without the legal system doing anything about it since enforcement will be too tough for the less serious crimes that are likely to be witnessed in VR and AR. To the layperson, virtual reality is merely a game. Courts and police departments may determine that the wrongdoing took place within the game or server and is a personal matter. The VR data will be owned by commercial corporations, who will impose terms of use that bind users and disclaim liability for harm. As a result, police will be even more hesitant to act. The capacity of VR and AR operators to contractually waive liability, together with 47 U.S.C. 230, will certainly deter lawsuits against them.
Virtual reality and augmented reality will also test our understanding of what constitutes speech, which is protected by the First Amendment, and what constitutes non-speech activity that requires regulation. Is nudity on a drive-in screen, speech, the same as indecent exposure, conduct? In the physical world, the basic distinction between words and actions makes sense because we believe that the harm that words may inflict at a distance is generally smaller and easier to avoid than the harm that physical touch can cause.
Virtual reality and augmented reality, on the other hand, are designed to make conveyed pictures and sounds feel as real as possible. They challenge our perception of reality because they blur the cognitive boundaries between imagery and physical existence. People react as if they’ve been slapped in the face when they receive a virtual slap. The reaction is intuitive; it is not based on actual physical contact, but it seems real in a way that words or images outside of VR do not.
With respect to injury in the actual and virtual worlds, VR and AR will offer legal challenges that may necessitate adjusting existing doctrines or changing legal laws. Now, I’d like to pose a question to you. Virtual reality isn’t “real” in the traditional sense. We see data that has been stitched together to create artificial audio and video. It does, however, feel real in a way that is difficult to explain until you’ve experienced it. The same might be said about augmented reality if it can overlay vibrant and lifelike representations of people and objects over the real-world reality we experience. Do you think we should punish specific types of conduct if a VR/AR misconduct experience feels genuine and has significant emotional and physiological consequences? How would you differentiate between virtual reality and physical wrongdoing in terms of punishment?
Why it Matters: Lawyers, the Spread of Misinformation and Social Media
It is important to remember the role lawyers play in and how the public views public figures, attorneys and the judicial system. This is especially true when posts are made on social media platforms or when statements are made available to the public in any manner. Many recent occurrences bring this important situation to light, most notably Rudy Giuliani’s unproven campaign regarding the “Big Lie” a/k/a the stolen election. Attorneys and important public figures may need to be held to a higher standard of care and accountability due to the public’s heavy reliance on the truth of their statements. Because of this reliance, social media companies, and the Courts, are forced into action to curb the spread of false information.
Facts on the spread of information on the internet. So many people now rely on social media as a way of communication and as a news source, which can sometimes be their only source. Information online can now spread faster than any other news source in history. The science behind the spread of information online, is quite astounding (and there is actual science behind it!).
A Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) study found that “It took the truth about six times as long as falsehood to reach 1500 people and 20 times as long as falsehood to reach a cascade depth of 10. As the truth never diffused beyond a depth of 10, we saw that falsehood reached a depth of 19 nearly 10 times faster than the truth reached a depth of 10.” These numbers show that false information spreads faster, farther and deeper than the truth. All users of social media are exposed and susceptible to false information, including attorneys, and our ability to discern true versus false information has become distorted leaving many users vulnerable.
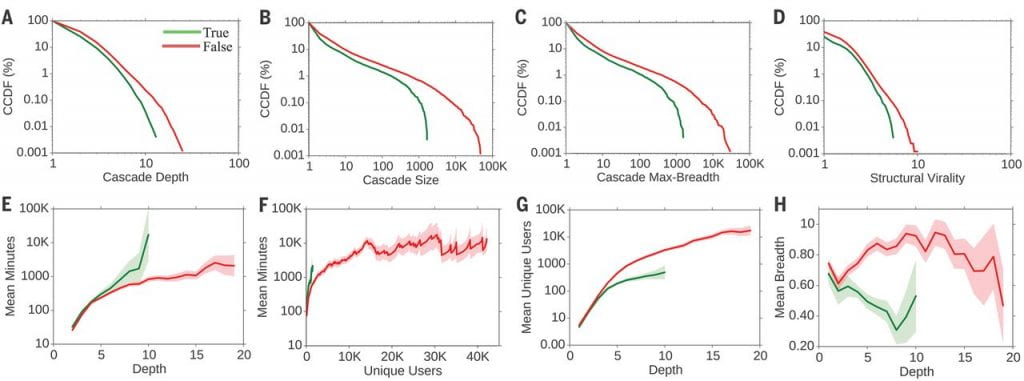
What causes of the spread of misinformation and who is susceptible? The American Psychological Association has published information on the causes of misinformation spreading and who is most susceptible. Researchers looked at individual differences and identified that “[b]roadly, political conservativism and lower levels of educational attainment are correlated with an increase in susceptibility to fake news.” Further, “[s]ix ‘degrees of manipulation’—impersonation, conspiracy, emotion, polarization, discrediting, and trolling—are used to spread misinformation and disinformation.” A false news story may quote a fake expert, use emotional language, or propose a conspiracy theory in order to manipulate readers.
People use the following five criteria to decide whether information is true: 1) compatibility with other known information, 2) credibility of the source, 3) whether others believe it, 4) whether the information is internally consistent, and 5) whether there is supporting evidence. The study also shows that people are more likely to accept misinformation as fact if it’s easy to hear or read. “We want people to understand that disinformation is fundamentally exploitative—that it tries to use our religion, our patriotism, and our desire for justice to outrage us and to dupe us into faulty reasoning,” says Peter Adams, News Literacy Project’s senior vice president of education. “Much of that is a psychological phenomenon.”This information may be helpful in understanding how a once highly respected lawyer and politician, is now the focus of discipline-committee-attention.
Rudy Giuliani. Social media is important to the legal profession because the court systems and attorneys use it to reach the public and potential clients. Consequently, it is of utmost importance to respect social media and to know how it functions to make it work for the intended purpose. Rudy Giuliani, attorney, former Mayor of New York City and personal counsel to President Trump, is the most prominent and current example of an attorney who used social media to spread misinformation. Giuliani is currently involved in numerous lawsuits for spewing a theory of election fraud that was ultimately disproved. Intriguingly, even though the claims lacked evidence to support them and were ultimately dispelled by the Judicial System, members of society believed these claims as truth while a large number of people still believe them.
Giuliani made these claims on mainstream media, his YouTube channel and seemingly anyone that would listen including Fox News. An anonymous source at Fox News stated, “We turned so far right we went crazy.” Giuliani reportedly earned monies making plugs to sell items during interviews and on his YouTube channel while making the statements at issue. Smartmatic filed suit against Rudy Giuliani and Fox News amongst others which is separate from the Dominion suit filed against Giuliani. These two suits encompass the same general claims, that Giuliani made false statements that the 2020 US Presidential election was stolen resulting in irreputable harm to companies.
Both the NYC Bar Association and the New York State Bar Association filed complaints against Mr. Giuliani requesting an investigation into his conduct.
The Appellate Division’s First Judicial Department of the New York Supreme Court suspended Giuliani’s law license on an interim basis in a June 24, 2021 decision concluding that his conduct threatened public interest. Not only did his behavior threaten public interest but it also tarnished the reputation of lawyers and the judicial system as a whole. The opinion further states, “When false statements are made by an attorney, it also erodes public confidence in the legal profession and its role as a crucial source of reliable information.”
Other examples of attorney epic-fails. An Illinois attorney wrote in her blog post referring to a judge as being “a total asshole,” and in another blog entry referred to a judge as “Judge Clueless.” The attorney also wrote about client specific cases and identified her clients by jail number or first name. That attorney received a 60 days suspension and was terminated from her employment as an Assistant Public Defender. Here, the attorney’s opinion, while it is hers and she has a right to it, could influence other court system employees, attorneys, judges or lay people entering the judicial system for whatever reason resulting in an influenced preconceived notion of the judge and the judge’s ability to render decisions in a case.
A Tennessee lawyer was suspended for 60 days for giving Facebook advise on how to kill and ex-boyfriend and make it look like self-defense while providing information on the new stand your ground law and the castle doctrine. Because a Florida lawyer made disparaging statements and accusations of judicial witchcraft, that attorney was disbarred and arrested!
Lawyers are held to a higher standard. Period. While Giuliani’s attorneys are arguing his right to make those statements are protected under his First Amendment right to free speech, “lawyers, as professionals, are subjected to speech restrictions that would not ordinarily apply to lay persons.” Especially, when it comes to judiciary review committees.
The legal system of attorneys is primarily a self-governing entity due to the professional legal standards inherent in the job. Attorneys swear an oath to support the Constitution of the United States before admission to practice. Attorneys are expected to uphold certain legal standards, enforce other attorneys to uphold those legal standards and, if necessary, report another attorney’s actions. A grievance committee is used to deter and investigate unethical conduct which can result in sanctions or commencement of a formal disciplinary proceeding at the Appellate Court level, as in the case of Mr. Giuliani’s interim suspension.
Rules to keep in mind as a practicing attorney. These rules come from the NY Rules of professional conduct.
- Rule 4.1 governs Truthfulness in Statements to Others and reads, in part, “In the course of representing a client, a lawyer shall not knowingly make a false statement of fact or law to a third person.”
- Rule 8.3 governs Reporting Professional Misconduct and reads in part, “(a) A lawyer who knows that another lawyer has committed a violation of the Rules of Professional Conduct that raises a substantial question as to that lawyer’s honesty, trustworthiness or fitness as a lawyer shall report such knowledge to a tribunal or other authority empowered to investigate or act upon such violation.”
- Rule 8.4 governs Misconduct and reads, in part, “A lawyer or law firm shall not: … (c) engage in conduct involving dishonesty, fraud, deceit or misrepresentation” and “(h) engage in any other conduct that adversely reflects on the lawyer’s fitness as a lawyer.”
What can be done to curb the spread of misinformation going forward? It seems inevitable that something has to give when it comes to social media and the downward spiral that may or may not hit rock bottom but only time will tell. Social media plays an important role in how our society communicates, shares ideas and inspires others. But is self-regulation enough? Should there be heightened standards for persons of influence? Should social media be regulated or are the companies sufficiently regulating themselves? Can the government work together with social media platforms to achieve a higher standard? Is judicial witchcraft even a thing? Regardless, your license to practice law is what it’s all about so choose your words wisely.
A Slap in the Face(book)?
Social media law has become somewhat of a contentious issue in recent years. While most people nowadays could not imagine life without it, many realize too, that it’s influence on our daily lives may not be a great thing. As the technology has advanced to unimaginable levels and the platforms have boomed in popularity, it seems as though our smart phones and Big Tech know our every move. The leading social media platform, Facebook, has around 1.82 billion active users a day, with people volunteering all sorts of personal information to be stored in the internet database. Individual profiles hold pictures of our children, our friends, our family, meals we eat, locations we visit. “What’s on your mind?” is the opening invite to any Facebook page, and one can only hazard a guess as to how many people actually answer that question on a daily basis. Social media sites know our likes, our dislikes, our preferences, our moods, the shoes we want to buy for that dress we are thinking of wearing to the party we are looking forward to in three weeks!
With all that knowledge, comes enormous power, and through algorithmic design, social media can manipulate our thoughts and beliefs by controlling what we see and don’t see. With all that power, therefore, should come responsibility, but Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act (CDA) has created a stark disconnect between the two. What started out as a worthy protection for internet service providers for the content posted by others, has more recently drawn criticism for the lack of accountability held by social media oligarchs such as Jack Dorsey (Twitter) and Mark Zuckerberg (Facebook).
However, that could all be about to change.
On May 28, 2017, three friends lost their lives in a deadly car accident in which the 17-year-old driver, Jason Davis, crashed into a tree at an estimated speed of 113 mph. Landen Brown, 20, and Hunter Morby, 17, were passengers. Tragic accident? Or wrongful death?
Parents of the deceased lay blame on the Snapchat App, which offered a ‘Speed Filter’ that would clock how fast you were moving, and allowed users to snap and share videos of their movements in progress.
You see where this is going.
As quickly became the trend, the three youths used the app to see how fast they could record the speed of their car. Just moments before their deaths, Davis had posted a ‘snap’ clocking the car’s speed at 123 mph. In Lemmon v Snap, the parents of two of the boys brought suit against the social media provider, Snap, Inc., claiming that the app feature encouraged reckless driving and ultimately served to “entice” the young users to their death.
Until now, social media platforms and other internet service providers have enjoyed the protection of near absolute immunity from liability. Written in 1996, Section 230 was designed to protect tech companies from liability, for suits such as defamation, for third party posts. In the early days, it was small tech companies, or an online business with a ‘comments’ feature that generally saw the benefits of the Code. 25 years later, many people are questioning the role of Section 230 within the vastly developing era of social media and the powerful pass it grants Big Tech in many of its societal shortcomings.
Regarded more as an open forum than the publisher or speaker, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, Instagram and Snapchat, have been shielded by Section 230 from any legal claims of harm caused by the content posted on their sites.
Applied broadly, it is argued that Section 230 prevents Snap, Inc. from being held legally responsible for the deaths of the three boys in this case, which is the defense the tech company relied upon. The district court dismissed the case on those grounds, holding that the captured speeds fall into the category of content published by a third party, for which the service provider cannot be held liable. The Ninth Circuit however, disagrees. The Court’s interesting swerve of such immunity, is that the speed filter resulted in the deaths of the boys regardless of whether or not their captured speeds were posted. In other words, it did not matter if the vehicle’s speed was shared with others in the app; the fact that the app promotes, and rewards, high speed (although the award system within the app is not entirely clear), is enough.
The implications of this could be tremendous. At a time when debate over 230 reevaluations is already heavy, this precedential interpretation of Section 230 could lead to some cleverly formulated legal arguments for holding internet service providers accountable for some of the highly damaging effects of internet, social media and smart phone usage.
For the many benefits the internet has to offer, it can no longer be denied that there is another, very ugly side to internet usage, in particular with social media.
It is somewhat of an open secret that social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram, purposely design their apps to be addictive by its users. It is also no secret that there is a growing association between social media usage and suicides, depression and other mental health issues. Cyber bullying has long been a very real problem. In addition, studies have shown that smart device screen time in very young children has shockingly detrimental impacts on a child’s social and emotional developments, not to mention the now commonly known damage it can have on a person’s eyesight.
An increased rate of divorces has been linked to smart phones, and distracted driving – whether it be texting or keeping tabs on your Twitter retweets, or Facebook ‘likes’– is on the increase. Even an increase in accidents while walking has been linked to distractions caused by the addictive smart devices.
With the idea of accountability being the underlying issue, it can of course be stated that almost all of these problems should be a matter of personal responsibility. Growing apart from your spouse? Ditch your cell phone and reinvent date night. Feeling depressed about your life as you ‘heart’ a picture of your colleague’s wine glass in front of a perfect sunset beach backdrop? Close your laptop and stop comparing yourself to everyone else’s highlights. Step in front of a cyclist while LOL’ing in a group text? Seriously….put your Apple Watch hand in your pocket and look where you are going! The list of personal-blame is endless. But then we hear about three young friends, two still in their teens, who lose their lives engaged with social media, and suddenly it’s not so easy to blame them for their own devastating misfortune.
While social media sites cannot be held responsible for the content posted by others, no matter how hurtful it might be to some, or no matter what actions it leads others to take, should they be held responsible for negligently making their sites so addictive, so emotionally manipulative and so targeted towards individual users, that such extensive and compulsive use leads to dire consequences? According to the Ninth Circuit, negligent app design can in fact be a cause of action for wrongful death.
With a potential crack in the 230-armor, the questions many lawyers will be scrambling to ask are:
-
-
- What duties do the smart device producers and/or internet service providers owe to their users?
- Are these duties breached by continuing to design, produce, and provide products that are now known to create such disturbing problems?
- What injuries have occurred and where those injuries foreseeably caused by any such breaches of duty?
-
For the time being, it is unlikely that any substantial milestone will be reached with regards to Big Tech accountability, but the Ninth Circuit decision in this case has certainly delivered a powerful blow to the Big Tech apparent untouchability in the courtroom.
As awareness of all these social media related issues grow, could this court decision open the door to further suits of defective or negligent product design resulting in death or injury? Time will tell…..stay tuned.
Is There Such a Thing as Off-Campus Anymore?
The Internet has given rise to considerable cyberbullying among students. Quite often the bullying occurs off-campus but is targeted at fellow students or administrators. The Third Circuit has previously considered and found in favor of free speech in two instances where students bullied school principals. Lisa S. Blatt, the attorney for the School Board, summed it up best during oral arguments; “When it comes to the Internet,” Blatt argued, “things like time and geography are meaningless.” Levy’s case presents the Court with the thorny issue of where the school steps start in our current virtual world.
Levy posted her Snapchat in 2017. At that time, schools were grappling with how to handle off-campus cyberbullying between classmates. Many authorities agree that under the Tinker standard, school officials can intervene if the off-campus speech has created or could create a substantial disruption or interference at school. Students have a right to feel secure on campus, and therefore a school has the power to discipline off-campus speech, even at the expense of a student’s right to free speech. Courts have applied this holding in a way that was favorable to the school to instances involving Internet chatter. In Rosario v. Clark County School Dist., a 2013 District Court upheld a school administration’s decision to discipline and punish a student for tweets a minor made while at a restaurant about a basketball coach who dismissed him from the team. In Kowalski v. Berkeley Cnty. Schs., the Fourth Circuit ruled that a school did not violate a student’s free speech rights by suspending her for creating and posting to a webpage that ridiculed fellow students.
On the other hand, in instances where students could prove in court that their off-campus social media did not substantially disrupt the school the student has prevailed. Consider, for example, Layshock v. Hermitage School Dist., in which the full Third Circuit ruled that the school infringed on a student’s First Amendment rights by suspending him for posting an online parody of the principle. The Court ruled the same way on almost the same set of facts in J.S. v. Blue Mountain School Dist. But to date, among Federal Circuit Courts, only the Third Circuit has sided with the school in instances of off-campus online speech. And even those cases suggest that there are instances where a school can appropriately infringe on a student’s First Amendment Rights. In response to J.S. and Layshock, Judge Kent Jordan of the Third Circuit stated: “The issue is whether the Supreme Court’s decision in Tinker, can be applied to off-campus speech. I believe it can, and no ruling coming out today is to the contrary.”
The Supreme Court could easily punt in this case; decide whether Levy’s Snapchat disrupted on-campus activities and leave it at that. But in this instance, the Court should not miss the opportunity to discuss the more significant issue of what rules should apply given the very real issue of blurred school boundaries. Especially since these boundaries have become even more blurred with the Pandemic. Living rooms and bedrooms across the country have become virtual classrooms. It seems impossible to suggest in today’s wired world that, as attorney Blatt suggests, there are any geographical boundaries to school. Prohibiting schools from regulating speech outside brick-and-mortar school buildings provides schools with the opportunity to prevent the severest of cyberbullying. On the other hand, expanding a schools’ reach threatens the very foundation of our constitution.
The Supreme Court decided Tinker well before the Internet was integral to our homes. Mahanoy Area School Dist. v. B.L., offers the Court the opportunity to provide much-needed guidance to school administrators who walk a tight balance between respecting First Amendment Rights and protecting the right of their students to learn in a conducive educational environment. Defining that guidance is the difficult part and with three new members of SCOTUS, it is hard to decide which way they may rule.
How do you think the Court should rule and what would your ruling be if you were a Supreme Court Justice?





