Social media allows millions of users to communicate with one another on a daily basis, but do you really know who is behind the computer screen?

As social media continues to expand into the enormous entity that we know it to be today, the more susceptible users are to abuse online. Impersonation through electronic means, often referred to as e-personation is a rapidly growing trend on social media. E-personation is extremely troublesome because it requires far less information than the other typical forms of identity theft. In order to create a fake social media page, all an e-personator would need is the victim’s name, and maybe a profile picture. While creating a fake account is relatively easy for the e-personator, the impact on the victim’s life can be detrimental.
E-personation Under State Law
It wasn’t until 2008, when New York became the first state to recognized e-personation as a criminally punishable form of identity theft. Under New York law, “a person is guilty of criminal impersonation in the second degree when he … impersonates another by communication by internet website or electronic means with intent to obtain a benefit or injure or defraud another, or by such communication pretends to be a public servant in order to induce another to submit to such authority or act in reliance on such pretense.”
Since 2008, other states, such as California, New Jersey, and Texas, have also amended their identity theft statutes to include online impersonation as a criminal offense. New Jersey amended their impersonation and identity theft statute in 2014, after an e-personator case revealed their current statute lacked any mention of “electronic communication” as means of unlawful impersonation. In 2011, New Jersey Superior Court Judge David Ironson in Morris County, declined to dismiss an indictment of identity theft against Dana Thornton. Ms. Thornton allegedly created a fictitious Facebook page that portrayed her ex-boyfriend, a narcotics detective, unfavorably. On the Facebook page, Thornton, pretending to be her ex, posted admitting to hiring prostitutes, using drugs, and even contracting a sexually transmitted disease. Thornton’s defense counsel argued that New Jersey’s impersonation statute was not applicable because online impersonation was not explicitly mentioned in the statute and therefore, Thornton’s actions do not fall within the scope of activity the statute proscribes. Judge Ironson disagreed by noting the New Jersey statute is “clear and unambiguous” in forbidding impersonation activities that cause injury and does not need to specify the means by which the injury occurs.
Currently under New Jersey law, a person is guilty of impersonation or theft of identity if … “the person engages in one or more of the following actions by any means, but not limited to, the use of electronic communications or an internet website:”
-
- Impersonates another or assumes a false identity … for the purpose of obtaining a benefit for himself or another or to injure or defraud another;
- Pretends to be a representative of some person or organization … for the purpose of obtaining a benefit for himself or another or to injure or defraud another;
- Impersonates another, assumes a false identity or makes a false or misleading statement regarding the identity of any person, in an oral or written application for services, for the purpose of obtaining services;
- Obtains any personal identifying information pertaining to another person and uses that information, or assists another person in using the information … without that person’s authorization and with the purpose to fraudulently obtain or attempt to obtain a benefit or services, or avoid the payment of debt … or avoid prosecution for a crime by using the name of the other person; or
- Impersonates another, assumes a false identity or makes a false or misleading statement, in the course of making an oral or written application for services, with the purpose of avoiding payment for prior services.
As social media continues to grow it is likely that more state legislators will amend their statutes to incorporate e-personation into their impersonation and identify theft statutes.
E-personators Twitter Takeover
Over the last week, e-personation has erupted into chaos on Twitter. Elon Musk brought Twitter on October 27, 2022, for $44 billion dollars. He immediately began firing the top Twitter executives including the chief executive and chief financial officer. On the verge of bankruptcy, Elon needed a plan to generate more subscription revenue. At last, the problematic Twitter Blue subscription was created. Under the Twitter Blue policy users could purchase a subscription for $8 a month and receive the blue verification check mark next to their Twitter handle. 
The unregulated distribution of the blue verification check mark has led to chaos on Twitter by allowing e-personators to run amuck. Traditionally the blue check mark has been a symbol of authentication for celebrities, politicians, news outlets, and other companies. It was created to protect those susceptible to e-personation. The rollout of Twitter Blue began on November 9, 2022, the policy did not specify any requirements needed to verify a user’s authenticity beyond payment of the monthly fee.
Shortly after the rollout, e-personators began to take advantage of their newly purchased verification subscription by impersonating celebrities, pharmaceutical companies, politicians, and even the new CEO of Twitter, Elon Musk. For example, comedian Kathy Griffin was one of the first Twitter accounts suspended after Twitter Blue’s launch for changing her Twitter name and profile photo to Elon Musk and impersonating the new CEO. Kathy was not the only Twitter user to impersonate Elon and in response Elon tweeted “Going forward, any Twitter handles engaging in impersonation without clearly specifying ‘parody’ will be permanently suspended.”
Elon’s threats of permanent suspension did not stop e-personators from trolling on Twitter. One e-personator used their blue check verification to masquerade as Eli Lilly and Company, an American pharmaceutical company. The fake Eli Lilly account tweeted the company would be providing free insulin to its customers. The real Eli Lilly account tweeted an apology shortly thereafter. 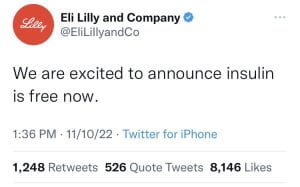 Another e-personator used their verification to impersonate former United States President George W. Bush. The fake Bush account tweeted “I miss killing Iraqis” along with a sad face emoji. The e-personators did not stop there, many more professional athletes, politicians, and companies were impersonated under the new Twitter Blue subscription policy. An internal Twitter log seen by the New York Times indicated that 140,000 accounts had signed up for the new Twitter Blue subscription. It is unlikely that Elon will be able to discover every e-personator account and remedy this spread of misinformation.
Another e-personator used their verification to impersonate former United States President George W. Bush. The fake Bush account tweeted “I miss killing Iraqis” along with a sad face emoji. The e-personators did not stop there, many more professional athletes, politicians, and companies were impersonated under the new Twitter Blue subscription policy. An internal Twitter log seen by the New York Times indicated that 140,000 accounts had signed up for the new Twitter Blue subscription. It is unlikely that Elon will be able to discover every e-personator account and remedy this spread of misinformation.
Twitter’s Term and Conditions
Before the rollout of Twitter Blue, Twitter’s guidelines included a policy for misleading and deceptive identities. Under Twitter’s policy “you many not impersonate individuals, groups, or organizations to mislead, confuse, or deceive others, nor use a fake identity in a manner that disrupts the experience of others on Twitter.” The guidelines further explain that impersonation is prohibited, specifically “you can’t pose as an existing person, group, or organization in a confusing or deceptive manner.” Based on the terms of Twitter’s guidelines, the recent e-personators are in direct violation of Twitter’s policy, but are these users also criminally liable?
Careful, You Could Get a Criminal Record
Social media networks, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, have little incentive to protect the interests of individual users because they cannot be held liable for anything their users post. Under section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, “no provider or user of an interactive computer service shall be treated as the publisher or speaker of any information provided by another information content provider.” Because of the lack responsibility placed on social media platforms, victims of e-personation often have a hard time trying to remove the fake online presence. Ironically, in order for a victim to gain control of an e-personator’s fake account, the victim must provide the social media platform with confidential identifying information, while the e-personator effectively remains anonymous.
By now you’re probably asking yourself, but what about the e-personators criminal liability? Under some state statutes, like those mentioned above, e-personators can be found criminally liable. However, there are some barriers that effect the effectiveness of these prosecutions. For example, e-personators maintain great anonymity, therefore finding the actual person behind the fake account could be difficult. Furthermore, many of the state statutes that criminalize e-personation include proving the perpetrator’s intent, which may also pose a risk to prosecution. Lastly, social media is a global phenomenon which means jurisdictional issues will arise when bringing these cases to court. Unfortunately, only a minority of states have amended their impersonation statutes to include e-personation. Hopefully as social media continues to grow more states will follow suit and e-personation will be prosecuted more efficiently and effectively. Remember, not everyone on social media is who they claim to be, so be cautious.
















 Last month, I wrote a
Last month, I wrote a 





